Lean data analytics processing is critical for advanced Business Intelligence in real-time with minimal latency and volatility. Managing a data management solution sourcing insights from disparate sources poses a huge challenge for organizations processing large bits of incoming and outgoing information. To keep up with growing organizational data processing systems, Operational Data Stores (ODS) have in-built features using on-demand insight processing tech. Migrating to ODS solutions improves data processing significantly, but analytical specialists must understand the basics of this solution first.
What is an Operational Data Store?
Operational Data Stores provide transactional insights rapidly despite gathering information from multiple sources. The main challenge enterprises face in data management is integrating legacy storage systems with cloud-based IaaS and/or SaaS solutions. Applications and analytical dashboards require real-time insights but with disparate sources gaining access to the needed data in a timely manner is complex.
Developers and data management experts can integrate multiple databases, but managing a system of this kind gets increasingly challenging over time. An ODS system resolves these challenges by integrating all databases and outputs any required data from an aggregated source. Developers can simultaneously query data from legacy systems and cloud-based storage systems on an application or analytical dashboard.
To answer the question, what is an ODS? It is a simplified solution to manage insights from disparate sources and avail the data to enterprise applications and Business Intelligence tools quickly with minimal volatility.
Main features of this solution
The main feature of ODS solutions is hosting transactional data using an on-demand system providing real-time insights to applications and dashboards. It is the leading solution for organizations with legacy storage systems that are gradually migrating to cloud-based solutions. This solution can facilitate a gradual transition from legacy storage systems to cloud-based technology instead of a rip and replace technique.
Other characteristics of Operational Data Stores are high availability and low fault tolerance. Unlike contemporary solutions, the insights written on an ODS are configurable and easily accessible. Data configuration happens in real-time, which is perfect for providing accurate insights to analytical dashboards.
The unique selling proposition of ODS systems boils down to this solution’s ability to aggregate insights from a wide range of sources simultaneously. This provides higher agility to applications and analytical dashboards instead of querying historical data that could be outdated at the time it is fetched.
Practical application scenarios
Think of the power enterprises can have with highly-available real-time insights gathered from multiple sources simultaneously. In addition, querying those real-time insights has minimal latency powering responsive applications with the required data right on time. There are countless practical application scenarios for ODS solutions, and one of them is powering advanced technology in education sector apps and software.
Educators can use ODS-powered performance review apps to notice improvement points students should work on. Operational Data Stores can gather insights from attendance register databases to digitized assessment and assignment results. In a corporate setting, ODS solutions provide a unified data source for advanced Business Intelligence enabling workgroups to make informed decisions using operational insights.
Instead of relying on weekly, biweekly, or even quarterly reports, businesses access real-time critical information guiding agile tactical decisions. The financial investments sector can benefit from ODS-powered dashboards integrating insights from multiple relevant sources at a time.
ODS vs. EDW
Operational Data Stores are not to be mistaken with Enterprise Data Warehouses (EDW). The infrastructure of these two data management solutions differs greatly, subsequently impacting their respective scopes of operations. An ODS functions as a catalyst for disparate storage systems, whereas an EDW hosts a variety of data management technologies stacked together.
Enterprise Data Warehouses can include an Operational Data Store as part of a full-stack solution. The infrastructure of EDWs includes data sources which could be CRM tools, ERPs, and legacy systems, and through ETL aggregated on an ODS. From there, the insights can be availed to a data warehouse and transferred to data marts.
Those data marts provide insights into BI tools or directly to user-end app interfaces. Therefore, an Operational Data Store can be used independently or as a subset of an Enterprise Data Warehouse used for multiple applications or Business Intelligence dashboards for real-time insights.
The technology behind Operational Data Stores
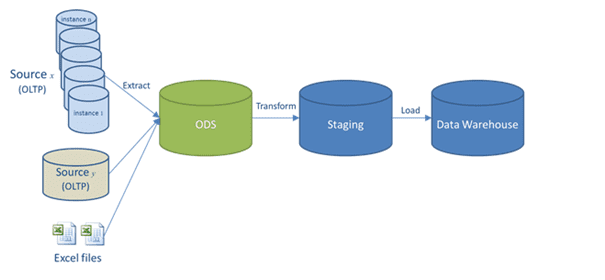
The main aim of this data management solution is to preserve data as-is from multiple disparate sources and present it to BI tools or user applications. Therefore, an ODS uses extracting and loading from the ETL process but skips transforming insights. ETL takes place in full once the information is being stored in a data warehouse from an Operational Data Store. When the data is in this management system, it is overwritten by incoming insights.
An ODS has the latest operational data currently applicable at that moment in time. Instead of using OLAP technologies, an ODS system utilizes OLTP to meet the global data needs of an enterprise. OLTP technology focuses on completing online transactions happening concurrently by fetching insights such as CRM insights and customer information from a central database.
As a result, an Operational Data Store can be used for e-commerce platforms and banking applications since these scenarios require operational transactional information. That information is overwritten as users make online transactions, and each transaction requires real-time updates. There are several other use cases for OLTP technology in an ODS aside from processing e-commerce and online banking transactions depending on the demands of a particular development project.
ODS advantages
ODS systems have the main benefit of eliminating batch processing that results from gathering insights on disparate sources using legacy systems. Batch processing generally results in higher latency rates and ultimately an unpleasant user experience on consumer-end user interfaces. Another benefit of using an ODS is greater flexibility in data sources that can be used and applications with access to querying insights from the store.
Subsequently, an ODS makes legacy data sources more scalable and have a wider scope of application. The ability to merge legacy data sources and cloud-based solutions gives Operational Data Stores a competitive advantage over other insight management systems.
Analysts and developers can access real-time operational insights to upload relevant information to reports and user-end application user interfaces. Additionally, analysts and reporting specialists can share data sources instead of having siloed insights which tend to limit the efficacy of reports generated using this outdated method.